What is CFD?
Computational Fluid Dynamics is the validation of fluid flow over a given specimen against various set flow conditions, environments and scenarios. In this instance the specimen is a static geometry which is then compared with the results of the Fluid Structure Interaction evaluation. Below is the initial FSI CFD with (A) represented with a simplified wing model and (B) the Full front wing.

Steady vs Transient CFD
To Illustrate the benefits of this analysis an initial transient model was constructed and compared with the standard steady state CFD. Below (A) represents the Full Front wing design in Steady state and (B) represents the resulting static geometry CFD in Transient.

What is Fluid Structure Interaction?
Unlike CFD where the geometry is static Fluid Structure Interaction allows for the assigning of properties to apply the computed loads from the aerodynamic forces to determine the deflected geometry for more accurate representation in Transient simulations.

Composite Properties
The materials used in this simulation include a 3ply configuration of carbon fiber laminated to the specification of the OBR25 Front wing design. For ease of simulation construction a Simplified wing model was first developed (left) then the full wing design was simulated (right)

Results
The results show a different level of performance to the transient simulations performed with static geometry. Along with a successful correlation includes a compliant level of deflection with accuracy to the displacement recorded on OBR25 regulation deflection test.


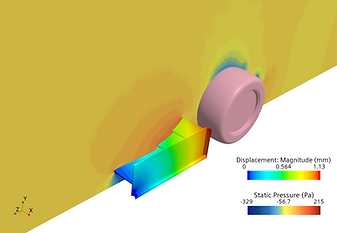
Aeromap
Implementing the simulation model with varying vehicle conditions provided a full representation of the Front wing movements by changing the vehicle's ride heights. Additional simulations also illustrated the compliance of the maximum allowable deflection with the highest performing Ride heights
Max Deflection

Max Downforce

Coefficient of Lift

Coefficient of Drag

